Age and can range from mild to severe Older children and adults with esotropia often have double vision (diplopia) When a person has esotropia without double vision, they do not have good depth perception This means that they are really only using the eye that can focus straight ahead to see What causes esotropia?Intermittent exotropia (X(T)) is one of the most common form of strabismus with surgery being the mainstay of treatment The main goal of surgery is to preserve binocular vision and stereopsis and to prevent its further loss The decision to operate is mainly based on four aspects increasing angle of exodeviation, deteriorating control of X(T), decrease in stereopsis for near or distance and Both groundin prisms and temporary stickon prisms have been described in the treatment of intermittent exotropia Basein prisms can be used to neutralize the deviation to stimulate fusion, or to overcorrect the deviation in the hope of reducing the deviation, 38 but this treatment modality is not commonly used today OverMinus Glasses
Squint Eye Treatment For Babies Children In Delhi
Mild exotropia treatment
Mild exotropia treatment- A simple definition of strabismus is misalignment of the eyes It is commonly called "crossed eyes" and affects five to 15 million people in the US alone() It includes any type of misalignment, such as one eye pointing in, out, up or down instead of in the same direction as the other eyeThankfully, many cases of strabismus can be improved with treatment The treatment of strabismus depends on the severity, and management options range from observation to surgery According to Michael Repka, MD, who is in practice at the Johns Hopkins Children's Center in Baltimore, "For small amounts of strabismus, prism correction and other optical approaches would be attempted first




Squint Eye Treatment Surgery In Delhi Best Strabismus Eye Doctor
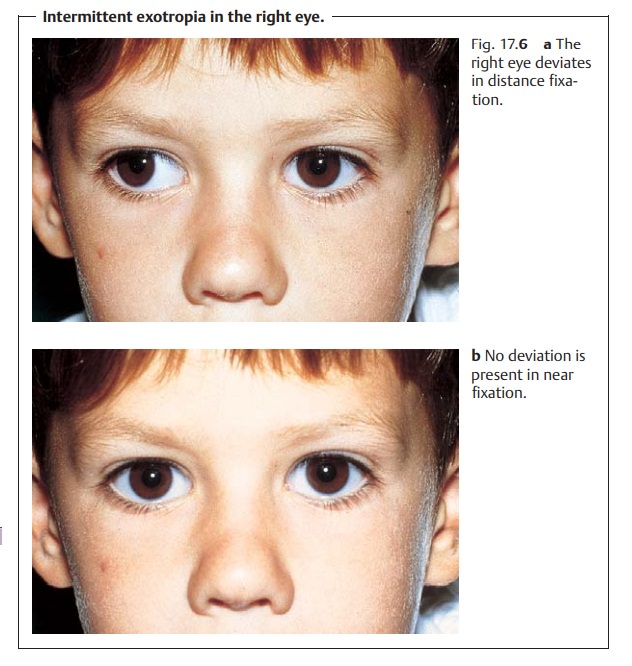
Intermittent exotropia Intermittent exotropia is a common type of strabismus that causes the eye to turn outward This type of eye turn may only be visible during stressful situations or when the person is tired, ill or anxious Advantages of an intermittent eye turnExotropia—or an outward turning of the eyes—is a common type of strabismus accounting for up to 25 percent of all ocular misalignment in early childhood Transient intermittent exotropia is sometimes seen in the first 4 6 weeks of life and, if mild, can resolve spontaneously by 6 8 weeks of agePurpose To compare the outcomes of unilateral lateral rectus recession to unilateral recessionresection in the treatment of patients with intermittent exotropia Methods The medical records of patients with intermittent exotropia with exodeviation of (Δ) to 25(Δ) who underwent unilateral lateral rectus recession or recessionresection at a single center from 02 to 10 were
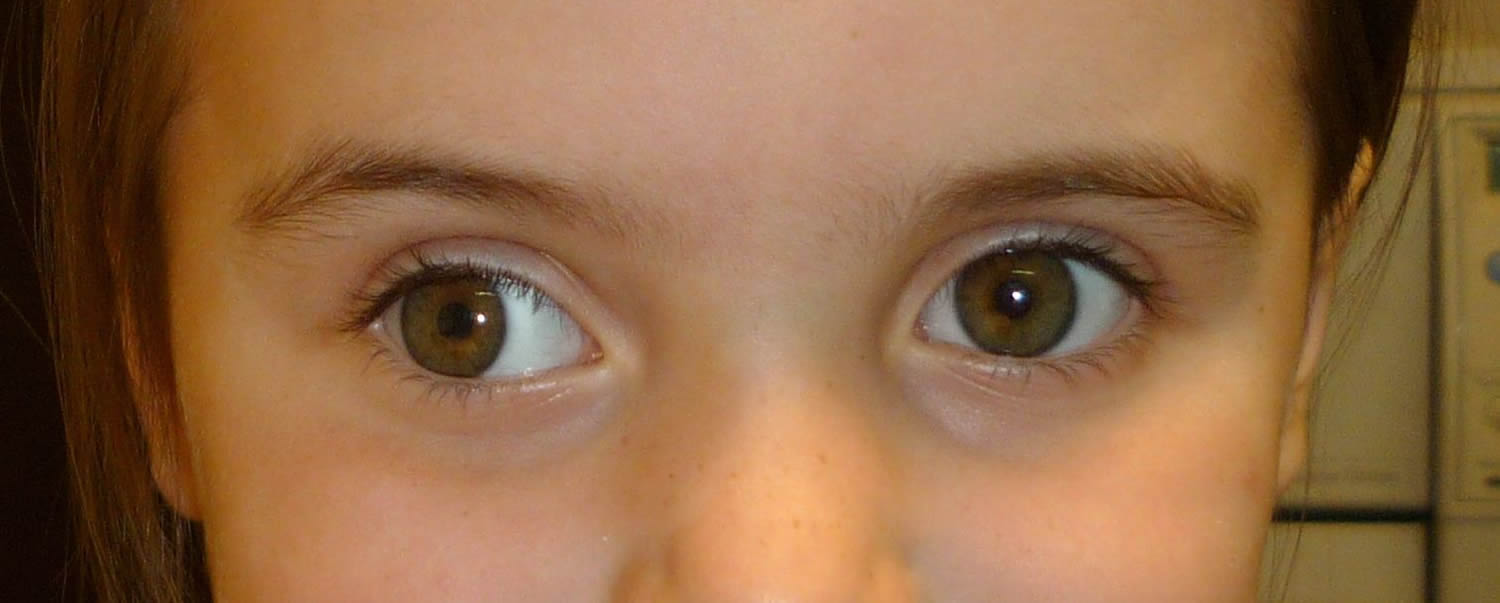
Answer Exophoria vs exotropia Exophoria and exotropia are closely related However, they aren't the same condition Exophoria is when one eye drifts outward during uneven visual stimulation or when viewing objects up close It's most common when only one eye is In the BT group (Table 1), 36 (419%) naïve patients not presenting with vertical ocular deviation, who had undergone chemodenervation before age 2 years (eight aged between 8 and 10 months, 26 aged between 12 and 24 months, and two older than 24 months), were enrolledThe outcome at 6 months was a complete success in 11 children (306%; If the condition is mild, it may go away on its own within 6 to 8 weeks of birth In other cases of exotropia, it is not common to find a complete resolution of the condition While patching, glasses, or vision therapy can help, exotropia may remain present
Exotropia can be constant or intermittent, severe or mild If left untreated, exotropia can worsen, and it is more difficult to treat in adults An optometrist may advise children with exotropia to wear glasses to correct their vision Exotropia can be difficult to detect, since it is not visible when a child is looking at a nearby object Mean distance intermittent exotropia (IXT) control score (the mean of 3 control scores) (primary outcome) The proportion of participants demonstrating a "treatment response," defined as ≥1 point improvement in the mean distance IXT control score without spontaneous exotropia during control testing (secondary outcome) Background The clinical management of intermittent exotropia has been discussed extensively in the literature, yet there remains a lack of clarity regarding indications for intervention, the most effective form of treatment and whether or not there is an optimal time in the evolution of the disease at which any treatment should be carried out




Strabismus Amblyopia Leukocoria Dr Hessah Alodan Pediatric Opthalmology




Eye Conditions That Cause Strabismus Optometrists Org
A Botulinum toxin injection b Corrective lenses c Occluding the affected eye for 6 hours per day d Patching of the unaffected eye for 2 hours Astigmatism is a common eye problem that can make your vision blurry or distorted It happens when your cornea (the clear front layer of your eye) or lens (an inner part of your eye that helps the eye focus) has a different shape than normal Learn about the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment of astigmatism10 A toddler exhibits exotropia of the right eye during a coveruncover screen The primary care pediatric nurse practitioner will refer to a pediatric ophthalmologist to initiate which treatment?




Complex Strabismus Ento Key




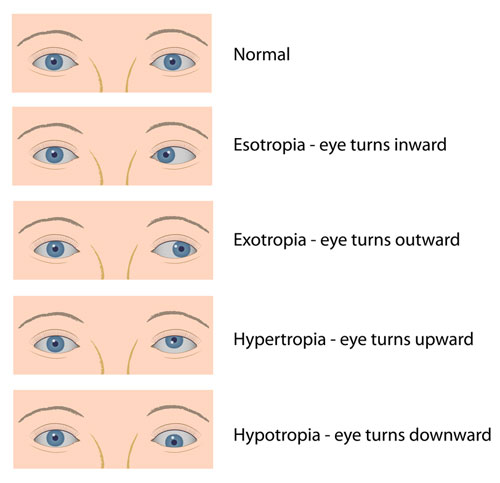
Esotropia
Botox injections Botox may be injected to realign the eyes of some people who have mild esotropia Exoforia treatment The exophoria or exotropia is mild, it is usually corrected, in the first instance, wearing glasses and performing visual therapy to improve eye movements The use of glasses or contact lenses is usually prescribed to people with exotropia who have, in turn, myopia or another refractive defect The treatment of infantile esotropia is extraocular muscle surgery Botulinum toxin (Botox ®) has been suggested as an alternative to surgery in patients with small to medium angle esotropia 13 Botox ® may also be used to augment the effects of extraocular muscle surgery 13




Management Of Intermittent Exotropia Of The Divergence Excess Type A Teaching Case Report The Journal Of Optometric Education




Exophoria
Eye turns, are also known as strabismus, and affect over 1 in babies and toddlers With early detection and eye care treatment, with eyeglasses and vision therapy, the eye turn can often be resolved, without relying on complicated eye surgeriesOPTOMETRIC CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE CARE OF THE PATIENT WITH STRABISMUS ESOTROPIA AND EXOTROPIA Reference Guide for Clinicians Prepared by the American Optometric Association Consensus PanelTreatments include Glasses Glasses that help correct near or farsightedness will help keep the eyes aligned Patching People with exotropia tend to favor the aligned eye, so vision in the eye turned outward can weaken, resulting Exercises Your doctor may suggest a




Esotropia




Exotropia Pediatric Ophthalmic Consultants
Treatment of intermittent exotropia Treatment recommendations depends on the severity of the problem, on the signs and symptoms, and on the patient and family desires When the drifting eye movement is mild, observation may be all that is needed Sometimes, the condition will remain the same over a long period of time or may even get better Treatment References Treatment for amblyopia includes one or more of the following patching, atropine eye drops, and optical penalization of the unaffected eye to stimulate visual developmentCommon sense approaches may help to control intermittent exotropia For example, getting the recommended amount of sleep for age is important—many children don't!




How To Fix Exotropia 9 Steps With Pictures Wikihow




Exotropia Eyes Turn Outward Causes Symptoms Treatment Vision Center
Treatments range from prescription eyewear to surgery to align the eyes However, many vision therapy programs now incorporate exercises for the eyes as well These can help to improve coordinationStaying as healthy as possible may also help Feeling sick or having a fever may cause the intermittent exotropia to temporarily occur more frequentlyExotropia treatment Treatment will vary depending on the severity of exotropia Some cases will have a relatively simple treatment plan, but others may require surgery Intermittent exotropia, which occurs occasionally, may only need to be monitored Nonsurgical exotropia treatment If exotropia is constant, an eye doctor may recommend




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




Exophoria
Oromandibular dystonia affects the muscles of the jaw, lips, and tongue It may cause difficulties with opening and closing the jaw, and speech and swallowing can be affected Spasmodic dysphonia, also called laryngeal dystonia, involves the muscles that control the vocal cords, resulting in strained or breathy speechExotropia is a type of strabismus (eye misalignment), where one eye turns, or deviates, outward (away from the nose) The deviation may be constant or intermittent, and the deviating eye may always be one eye or may alternate between the two eyes The deviation or eye turn may occur while fixating (looking at) distant objects, near objects, or bothVision therapy for both patients consisted of weekly inoffice sessions each lasting 45 minutes, followed by 15 minutes of daily home therapy activities The first five weeks of vision therapy focused on antisuppression, diplopia awareness, gross convergence, and increasing the amplitudes of accommodation




Squint Eye Treatment For Babies Children In Delhi




Strabismus Children S Health Issues Msd Manual Consumer Version
To investigate the clinical features and obtain guideline of treatment in intermittent exotropia associated with hypertropia including simulated superior oblique palsy We retrospectively reviewed Exotropia—or an outward turning of the eyes—is a common type of strabismus accounting for up to 25 percent of all ocular misalignment in early childhoodTransient intermittent exotropia is sometimes seen in the first 4 – 6 weeks of life and, if mild, can resolve spontaneously by 6 – 8 weeks of age In Exotropia the Eyes are deviated outwards It causes Double Vision and tiredness in the Eyes It is associated with Squint and Strabismus There are three types of Exotropia Congenital Strabismus It is present by birth It may be due to genetic disorders Intermittent Exotropia It may be seen in day dreaming




Infantile Esotropia Management Youtube




Exotropia Types Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prevention
Basic intermittent exotropia can be treated in various ways Vision Therapy is a worthwhile option Surgical correction and overminus treatment have also been effective treatments Assessment should include the intermittent exotropia control scale and the convergence insufficiency symptom survey Vision therapyFor mild cases of exotropia, eyelasses and/or vision therapy (eye exercises) are the most common treatment methods Eyeglasses are used to make each eye see as well as possible so that the eyes will work together as a teamHow common is intermittent exotropia?




Medial Rectus Plication Versus Resection In Adults With Exotropia Gaballah Ka J Egypt Ophthalmol Soc



Forms Of Concomitant Strabismus
4 Try the brock string exercise to improve eye coordination and focus Tie a 5 ft (15 m) string to a chair or rail and slide three beads that are about 1 inch (25 cm) in size onto the string so they're at least 1 foot (30 cm) apart Then hold the other end of the string near your nose so the string is tautTreatment for exotropia depends on how often you have symptoms and on how severe they are Prism in your glasses may be prescribed to help with double vision Eye muscle surgery is also an option, especially if your exotropia is Kellogg Eye Center Exotropia 2!!An adult with strabismus will experience double vision The onset can be sudden or gradual, says Dr Howard The distortion may occur only sometimes or in specific circumstances Strabismus may be intermittent at first and then become constant "It may only happen when you look in a particular direction," says Dr Howard



Management Of Strabismus In Myopes Kekunnaya R Chandrasekharan A Sachdeva V Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol




Exotropia Pediatric Ophthalmic Consultants
Among the treatment options for esotropia are Glasses to correct vision problems such as nearsightedness, farsightedness or astigmatism Patching of the good eye, to improve vision in the lazy (amblyopic) eye Surgery on the eye muscles to realign the eyesEsotropia is a strabismus condition where the eye turns inward (toward the nose) This condition may be evident intermittently (not all the time) or constantly The deviation, or eye turn, may occur while fixating (looking at) distance objects, near objects, or




How To Fix Exotropia 9 Steps With Pictures Wikihow



Intermittent Exotropia



Strabismus Optometrist Optical Shop



1




An Example Of Constant Exotropia A Subtype Of Strabismus Download Scientific Diagram




Exotropia Pediatric Ophthalmic Consultants
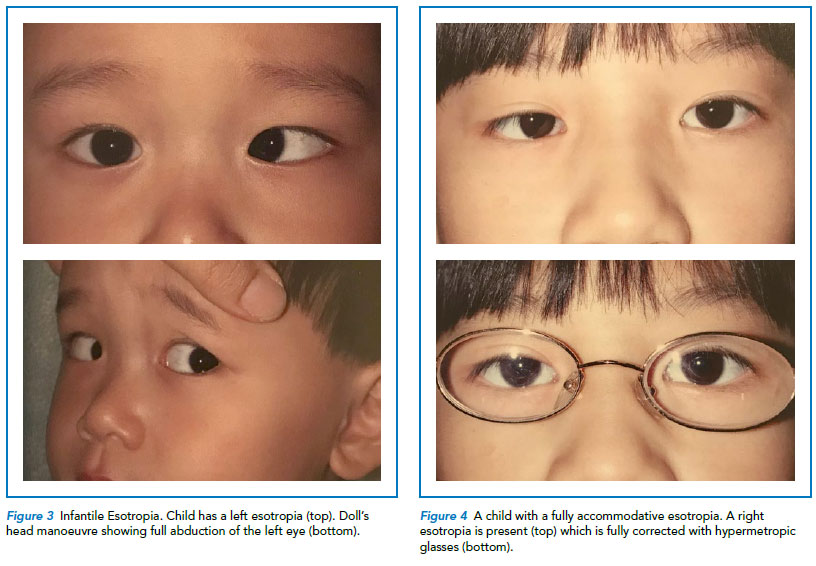



Common Strabismus In Children A Brief Overview Singhealth




Exotropia Pediatric Ophthalmic Consultants




Non Accommodative Esotropia And Botulinum Toxin Therapy




How To Fix Exotropia 9 Steps With Pictures Wikihow




Exotropia Pediatric Ophthalmic Consultants




Exotropia Pediatric Ophthalmic Consultants




Management Of Intermittent Exotropia Of The Divergence Excess Type A Teaching Case Report The Journal Of Optometric Education




Exotropia In Children And Adults




Exotropia Outward Eye Turn
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/esotropia584188178-5a47bd82beba330037d008c3.jpg)



Esotropia Causes Types And Complications




Intermittent Exotropia




Strabismus Treatment Gallaway Beckett Vision Therapy New Jersey Philadelphia
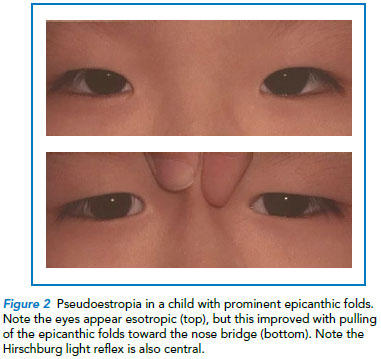



Common Strabismus In Children A Brief Overview Singhealth




Special Forms Of Comitant Exotropia Ento Key




Exotropia Eyewiki




Strabismus Amblyopia Leukocoria Saeed Alwadani Md Assistant Professor




Strabismus Cigna




How To Fix Exotropia 9 Steps With Pictures Wikihow




Accommodative Esotropia American Association For Pediatric Ophthalmology And Strabismus




Squint Eye Treatment Surgery In Delhi Best Strabismus Eye Doctor



1



Hypertropia




Exotropia Symptoms Management And More




Providers In Charlotte Who Treat Strabismus



Exotropia Outward Eye Turn
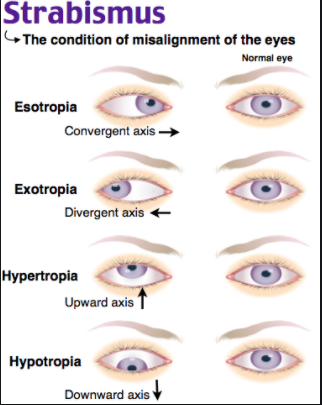



Orchidia Strabismus




Pdf Characteristics Of Patients Who Are Not Responsive To Alternate Patching For Overcorrected Intermittent Exotropia




Providers In Charlotte Who Treat Strabismus




Esotropia Cross Eyed And Its Causes And Symptoms Vision Express




What Is Intermittent Strabismus Optometrists Org
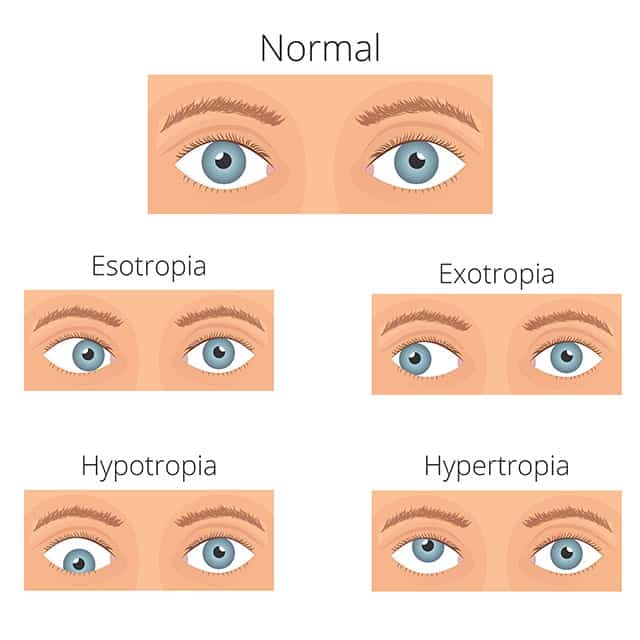



Esotropia Everyday Sight



Exotropia Pediatric Ophthalmic Consultants



Non Accommodative Esotropia And Botulinum Toxin Therapy



Strabismus Wikipedia




Exodeviations An Exodeviation Is A Divergent Strabismus That




Medial Rectus Plication Versus Resection In Adults With Exotropia Gaballah Ka J Egypt Ophthalmol Soc




Strabismus Natural Ways To Help Resolve Crossed Eyes Dr Axe




Esotropia Alternating And Intermittent Types And Treatment Options



Exotropia Pediatric Ophthalmic Consultants




Pdf Consecutive Exotropia After Convergent Strabismus Surgery Surgical Treatment




Exophoria Definition Treatment And How It Compares To Exotropia



1




What Is Exotropia Vision Express




Management Of Intermittent Exotropia Of The Divergence Excess Type A Teaching Case Report The Journal Of Optometric Education




How To Take On Strabismus In Adults




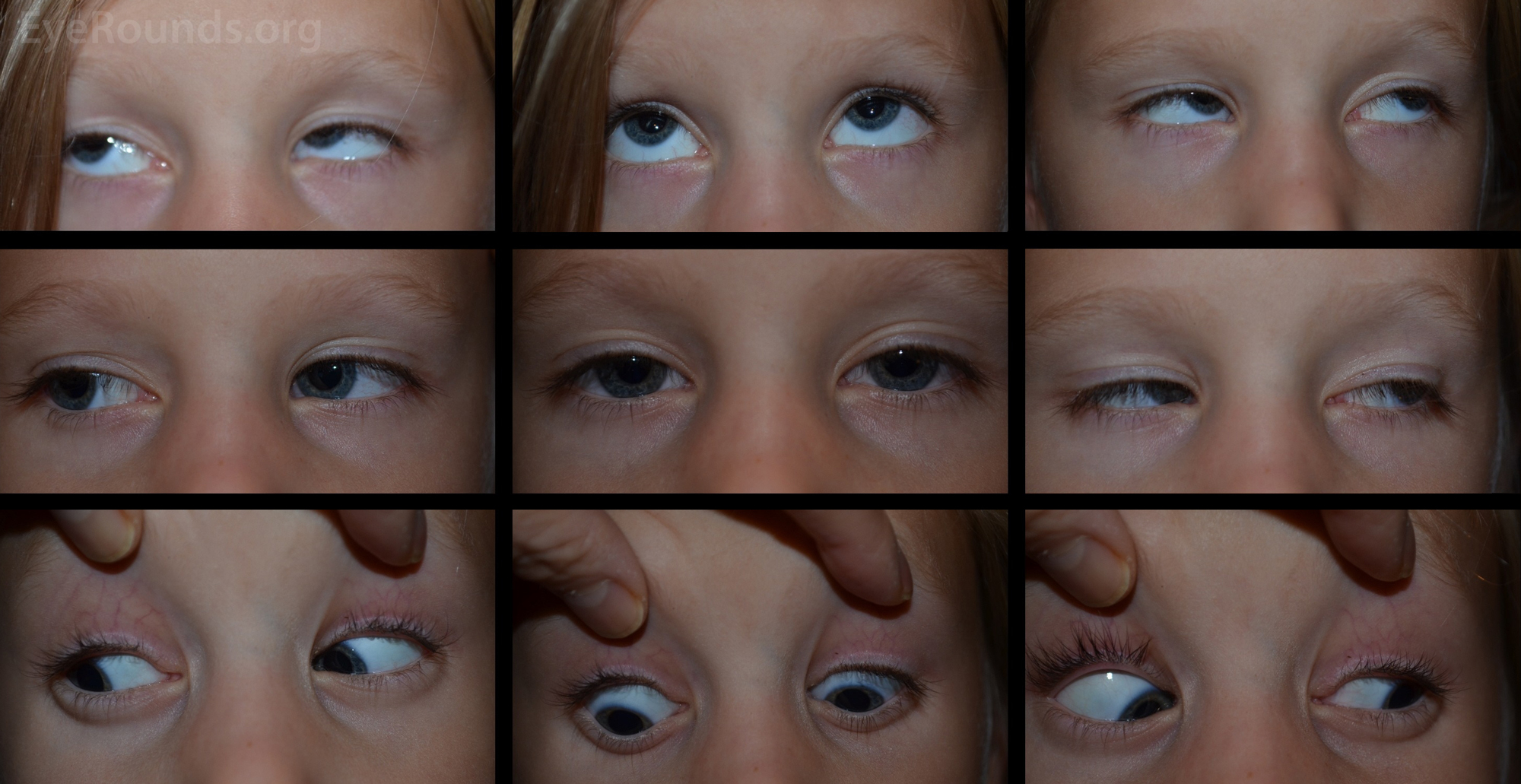
Initial Photograph Of The Patient Shows Mild Ptosis Exotropia And Download Scientific Diagram




Fixing Aloise S Gaze Strabismus Wow Vision Therapy Youtube
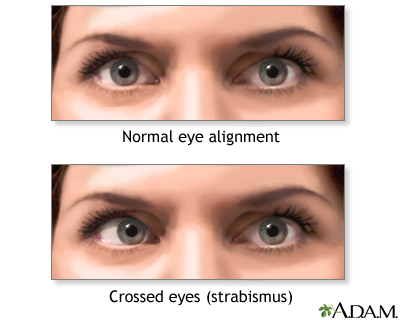



Strabismus Information Mount Sinai New York




Acute Acquired Comitant Esotropia In Adults Is It Neurologic Or Not
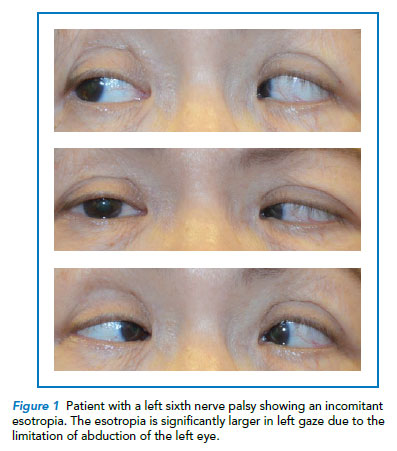



Common Strabismus In Children A Brief Overview Singhealth



Strabismus Ananthaksha Super Speciality Eye Hospital




Surgical Planning For Duane Retraction Syndrome




Esotropia Types Symptoms And Treatment
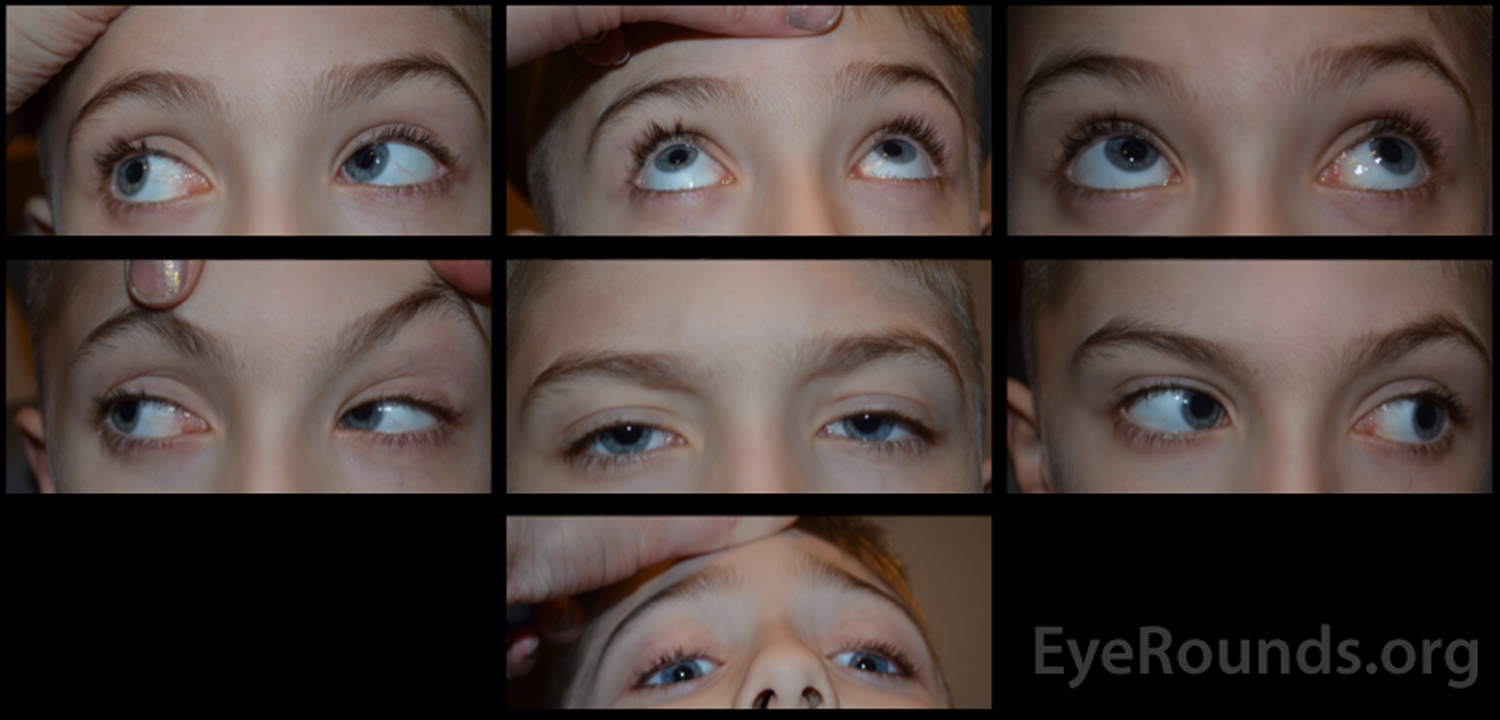



Non Accommodative Esotropia And Botulinum Toxin Therapy




Special Forms Of Comitant Exotropia Ento Key




Control Of Intermittent Exotropia Should Be Assessed With Control Of Intermittent Exotropia Should Be Assessed With




How To Fix Cross Eyes Naturally Image Optometry




Management Of Intermittent Exotropia Of The Divergence Excess Type A Teaching Case Report The Journal Of Optometric Education




Comitant Esodeviations An Update
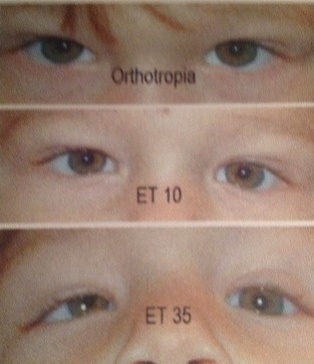



Principles Of Strabismus Surgery For Common Horizontal And Vertical Strabismus Types Intechopen




Strabismus Crossed Eyes All About Vision




Medial Rectus Plication Versus Resection In Adults With Exotropia Gaballah Ka J Egypt Ophthalmol Soc
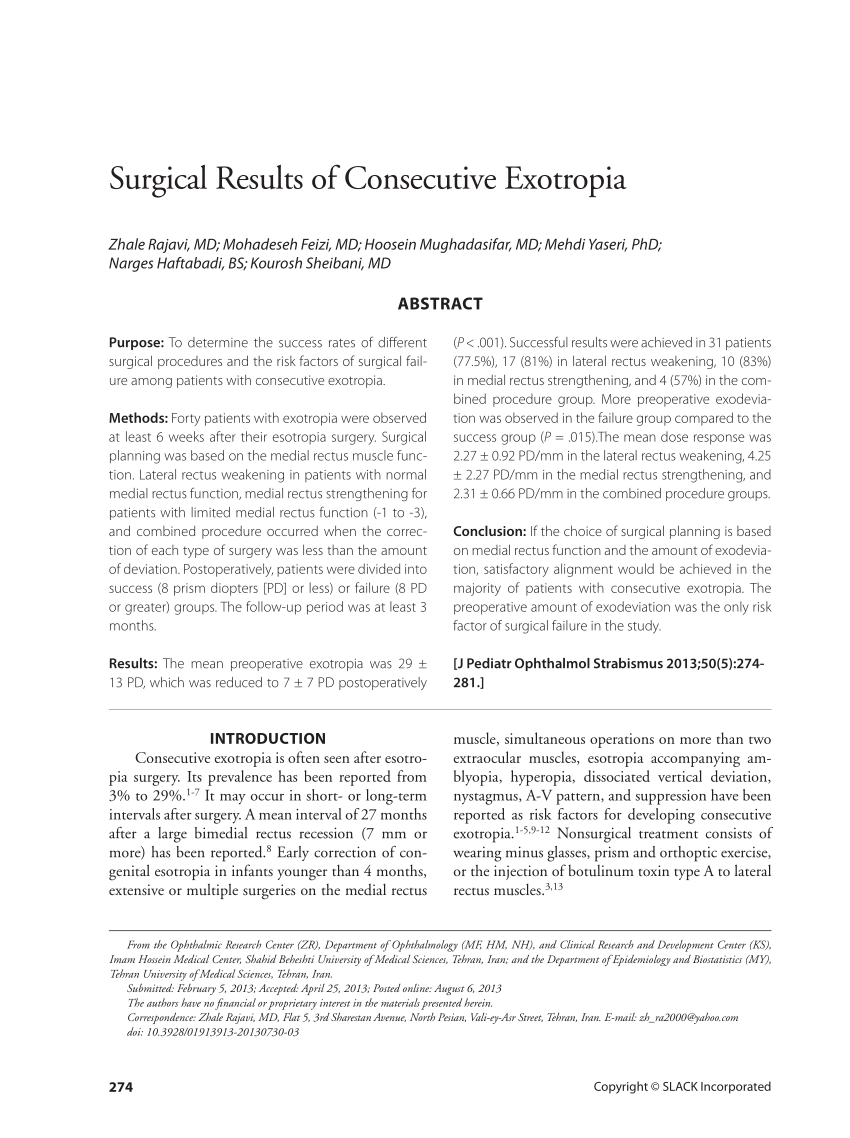



Pdf Surgical Results Of Consecutive Exotropia




How To Fix Exotropia 9 Steps With Pictures Wikihow




Strabismus Amblyopia Leukocoria Saeed Alwadani Md Assistant Professor




How To Fix Exotropia 9 Steps With Pictures Wikihow




Medial Rectus Plication Versus Resection In Adults With Exotropia Gaballah Ka J Egypt Ophthalmol Soc




Exotropia American Association For Pediatric Ophthalmology And Strabismus




3 Eye Exercises For Strabismus Healthline




Principles Of Strabismus Surgery For Common Horizontal And Vertical Strabismus Types Intechopen



Lazy Eye Exercises 8 Exercises And Other Treatments




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader
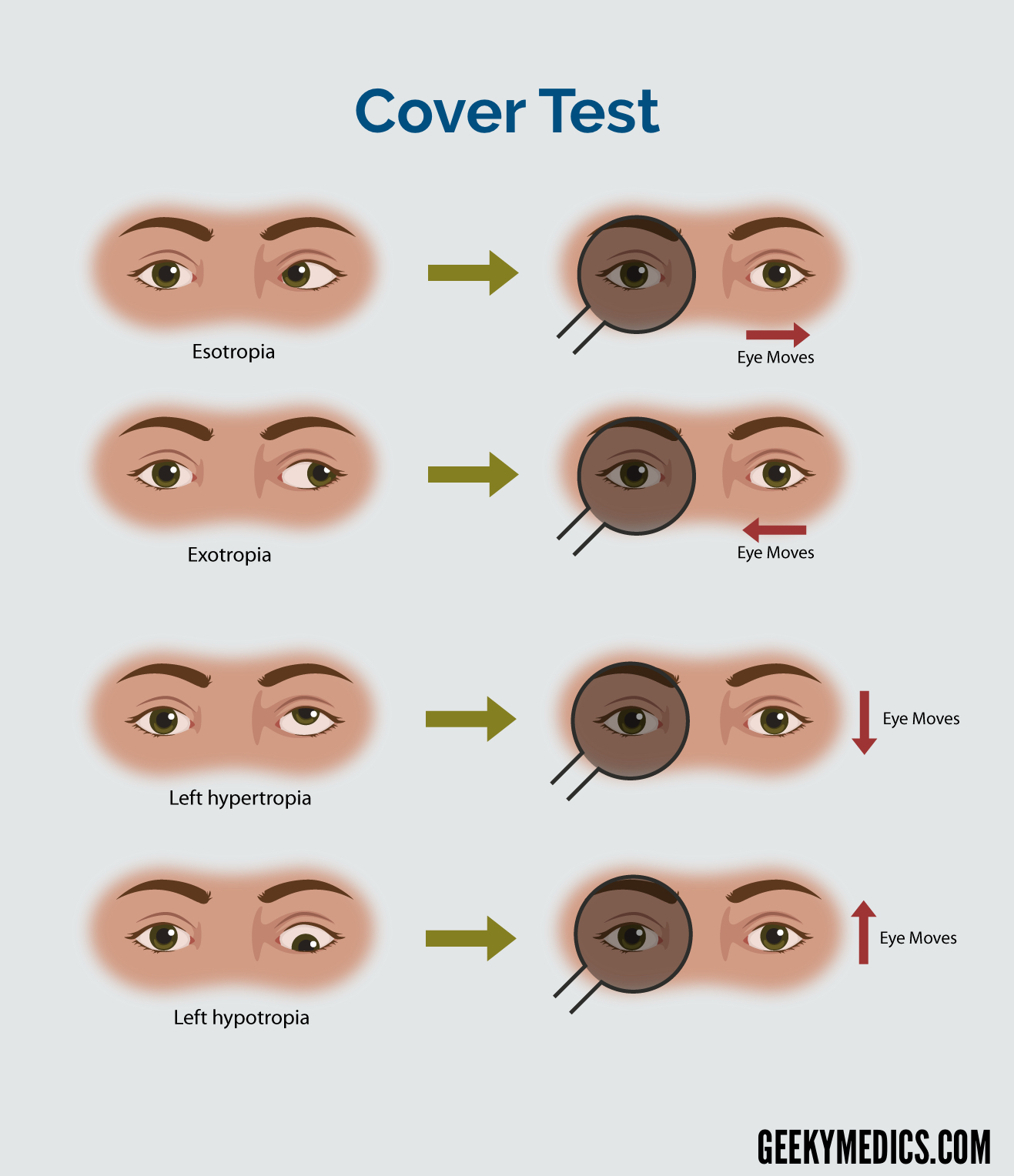



Strabismus Exotropia Esotropia Cover Test Geeky Medics
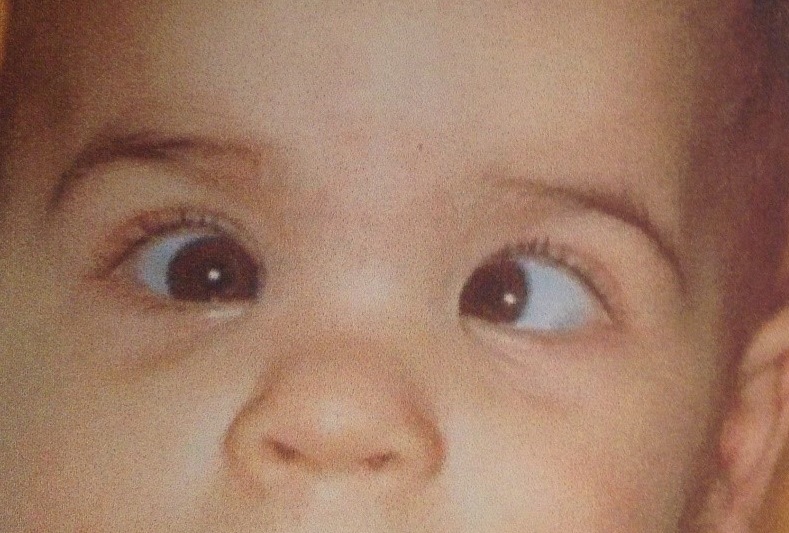



Principles Of Strabismus Surgery For Common Horizontal And Vertical Strabismus Types Intechopen




Strabismus Amblyopia Leukocoria Dr Hessah Alodan Pediatric Opthalmology



Pdf Consecutive Exotropia After Convergent Strabismus Surgery Surgical Treatment




Principles Of Strabismus Surgery For Common Horizontal And Vertical Strabismus Types Intechopen




Exotropia Psychology Wiki Fandom


